Dnd (电子游戏)
外观
| dnd | |
|---|---|
| 类型 | 角色扮演 |
| 平台 | 柏拉图系统 |
| 开发商 | Gary Whisenhunt, Ray Wood |
| 发行日 | 1975 |
《dnd》是一款电子角色扮演游戏。其名“dnd”源自1974年首发桌上角色扮演游戏《龙与地下城》的缩写“DND”(D&D)。
电子游戏《dnd》由盖瑞·威森亨特和瑞·伍德于1974年到1975年在南伊利诺伊大学,用TUTOR程序语言为柏拉图系统编写[1][2]。爱荷华州立大学的德克·佩利特与伊利诺伊大学的弗林特·佩利特在1976到1985年间接着强化游戏。[3]
玩法
[编辑]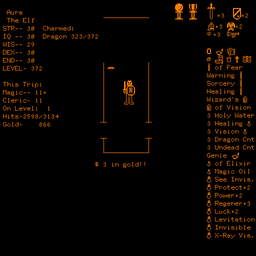
在《dnd》中,玩家将创建一个角色并冒险进入多层威森伍德地牢(Whisenwood,两个作者姓氏的混成詞),以寻找两个终极宝藏:圣杯和宝珠。[5]。游戏为玩家提供了地牢的俯视图,还实现了龙与地下城的许多基本概念。 威森伍德地牢由多个迷宫状的楼层组成。 随着玩家完成每个楼层,他们可以前进到下一个楼层。 但是,玩家也可以返回到先前的楼层并离开地牢,这使《dnd》成为最早使用非线性进程的电子游戏之一。 当玩家完成一个楼层后,他们将获得新的咒语,武器和物品,以帮助他们完成寻找终极宝藏的任务。
传送者会在地牢之间移动角色。 每个地牢的尽头都有高等级的怪物,包括守卫宝珠的金龙。 离开地牢可以使角色恢复体力与法力并在稍后返回。
参考文献
[编辑]- ^ Mark J. P. Wolf Before the Crash: Early Video Game History 2012 p212 "After Spacewar!, several more games appeared on the PLATO system, including DECWAR (1974, based on “Star Trek”), Empire (1974), a Dungeons & Dragons–inspired game named "dnd" released in 1979, Moria (1975), the original Freecell (1978), and a flight simulator named Airfight..."
- ^ Martell, Carey. Interview with creators of dnd (PLATO). www.Rpgfanatic.net. [4 May 2012]. (原始内容存档于2013-10-27).
- ^ Dear, Brian. Chapter 16: Into the Dungeon. The Friendly Orange Glow: The Untold Story of the PLATO System and the Dawn of Cyberculture. New York: Pantheon Books. 2017: 294–297 [2021-02-21]. (原始内容存档于2021-03-04).
- ^ Gary Whisenhunt, Ray Wood, Dirk Pellett, and Flint Pellett's DND (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆). The Armory (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆). Retrieved on 2008-04-08.
- ^ 5.0 5.1 dnd (The Game of Dungeons) (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆).Universal Videogame List (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆). Retrieved on 2008-04-09.
来源
[编辑]- "Retro Playing Games", Computer Games, April, 2006, p. 36–37.
外部链接
[编辑]- cyber1.org (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆) – 《dnd》以及其他许多地牢类游戏都可以在这个网站上进行游玩。
